 Transmission Gate
Transmission Gate
| Library: | Wiring |
| Introduced: | 2.7.0 |
| Appearance: |
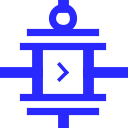
|
Behavior
A transmission gate has three inputs, called source, n-gate, and p-gate; and it has one output, called drain. When diagrammed, the source input and drain output are drawn connected by two plates; Logisim draws an arrowhead to indicate the direction of flow from input to output. The two gate inputs are drawn as lines connected to plates parallel to each of the plates connecting source to drain. The p-gate input's line has a circle, while the n-gate input's line does not.
| p-gate | ||
| source |

|
drain |
| n-gate |
The transmission gate is simply the combination of two complementary transistors. Indeed, the same behavior can be achieved in Logisim by using just one transistor. However, designers sometimes prefer to use matched pairs of transistors due to electrical issues with draining voltage that is more complex than Logisim attempts to simulate.
The values at n-gate and p-gate are expected to be opposite to each other. If p-gate is 0 while n-gate is 1, then the value found at source is transmitted to drain. If p-gate is 1 while p-gate is 0, then the connection is broken, so the value at drain is left floating. In all other cases, drain receives an error output — unless source is floating, in which case drain is floating as well. This behavior is summarized by the following table.
| p-gate | n-gate | drain |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | * |
| 0 | 1 | source |
| 1 | 0 | U |
| 1 | 1 | * |
| U/E | all | * |
| all | U/E | * |
* If source is High impedance (U), drain is High impedance (U) otherwise drain is in error (E).
Note:Since Logisim uses the markers U (High impedance) and E (Error) I used the same in the illustrations rather than the more common Z (High impedance) and X (Error) in other documents
If the Data Bits attribute is more than 1, each gate input is still a single bit, but the gate values are applied simultaneously to each of the source input's bits.
Pins
This component has four pins, three are inputs Source,P-gate and N-gate one is an output Drain which you can see in the figure above.
- West edge: The source
- The component's source input that will transmit to the output if triggered by the p-gate and n-gate inputs. Bit width matches Data Bits attribute.
- North edge: p-gate
- The component's p-gate input, controls the transmission. Normally, opposite control values are applied to these inputs. The bit width is 1.
- South edge: n-gate
- The component's n-gate input, controls the transmission. Normally, opposite control values are applied to these inputs. The bit width is 1.
- East edge: The drain
- The component's output, which will match the source input if p-gate is 0 and n-gate is 1, or it will be floating (U) if p-gate is 1 and n-gate is 0. For all other values on p-gate and n-gate, the output is an error value (E). Bit width matches Data Bits attribute.
Attributes
When the component is selected or being added, Alt-0 through Alt-9 alter its Data Bits attribute and the arrow keys alter its Facing attribute.
- Facing
- The direction of the component its output relative to input.
- Gate Location
- The location of the gate input.
- Data Bits
- The bit width of the component's inputs and outputs.
Poke Tool Behavior
None.
Text Tool Behavior
None.
Back to Library Reference